Is Image Scraping Legal? (Everything You Need to Know)
Understand the legal implications of image scraping and web scraping. Learn about copyright law, fair use, and best practices for legal image extraction.

Image scraping and web scraping raise important legal questions that every user should understand. While the technology makes it easy to download images from websites, the legal landscape is complex and varies by jurisdiction. This comprehensive guide explains what's legal, what's not, and how to stay compliant.
Understanding the Legal Landscape
Image scraping legality depends on several factors:
- Copyright law: Most images are protected by copyright
- Website terms of service: What the website allows or prohibits
- Fair use exceptions: Limited circumstances where use is permitted
- Jurisdiction: Laws vary by country and region
- Intended use: Commercial vs. personal vs. educational purposes
Copyright Law Basics
Copyright protection applies to most images automatically:
- Automatic protection: Copyright exists from the moment of creation
- No registration required: Images don't need to be registered
- Duration: Typically lasts for creator's life plus 70 years
- Exclusive rights: Only copyright owner can reproduce, distribute, or display
- International protection: Most countries respect international copyright treaties
What Constitutes Copyright Infringement
You may be infringing copyright if you:
- Download images without permission: Unless fair use applies
- Use images commercially: Without proper licensing
- Modify copyrighted images: Without authorization
- Distribute images widely: Beyond personal use
- Remove copyright notices: Or attribution information
Fair Use Exceptions
Fair use provides limited exceptions to copyright protection:
Educational Use:
- Academic research: Using images for scholarly work
- Classroom teaching: Educational presentations and materials
- Student projects: Academic assignments and research
- Non-profit education: Educational institutions and programs
Research and Criticism:
- Art criticism: Analyzing and commenting on images
- News reporting: Using images in news articles
- Parody and satire: Transformative use for commentary
- Historical analysis: Using images for historical research
Personal Use:
- Personal reference: Using images for personal study
- Non-commercial projects: Personal creative work
- Research and learning: Personal educational purposes
Website Terms of Service
Website terms can create additional legal obligations:
- Acceptance of terms: Using a website may bind you to its terms
- Prohibited activities: Many sites explicitly ban scraping
- Rate limiting: Terms may limit how many requests you can make
- Commercial restrictions: May prohibit commercial use of content
- Attribution requirements: May require crediting the source
Legal Image Scraping Methods
There are several ways to legally obtain images:
1. Public Domain Images
- Expired copyright: Images whose copyright has expired
- Government works: Many government images are public domain
- Creative Commons Zero: Images explicitly released to public domain
- Historical images: Very old images may be public domain
2. Creative Commons Licensed Images
- CC BY: Attribution required, but commercial use allowed
- CC BY-SA: Attribution and share-alike required
- CC BY-NC: Attribution required, non-commercial use only
- CC BY-ND: Attribution required, no derivatives allowed
3. Properly Licensed Images
- Stock photo licenses: Purchase licenses for commercial use
- Direct permission: Contact image owners for permission
- License agreements: Formal licensing contracts
- Royalty-free licenses: One-time payment for unlimited use
Best Practices for Legal Compliance
Follow these guidelines to stay within legal boundaries:
Before Scraping:
- Check copyright status: Verify if images are protected
- Read website terms: Understand what's allowed
- Look for licensing information: Check for Creative Commons or other licenses
- Contact owners: Ask for permission when in doubt
- Document your research: Keep records of your compliance efforts
During Scraping:
- Respect robots.txt: Follow website crawling policies
- Use reasonable rates: Don't overwhelm servers
- Preserve metadata: Keep copyright and attribution information
- Limit scope: Only scrape what you need
- Monitor for changes: Stay updated on website terms
After Scraping:
- Proper attribution: Credit original creators when required
- Respect usage restrictions: Follow license terms
- Monitor for takedown requests: Respond promptly to complaints
- Keep records: Document your legal basis for use
International Legal Considerations
Laws vary significantly by country:
United States:
- Fair use doctrine: More flexible than many countries
- DMCA: Digital Millennium Copyright Act protections
- State variations: Some states have additional protections
European Union:
- GDPR considerations: Data protection regulations
- Stricter fair use: More limited exceptions
- Database rights: Additional protections for collections
Other Jurisdictions:
- Canada: Fair dealing doctrine
- Australia: Fair dealing with specific exceptions
- Japan: Limited fair use provisions
Risks and Consequences
Understanding the potential consequences:
Legal Risks:
- Cease and desist letters: Formal requests to stop
- DMCA takedowns: Removal of content from platforms
- Lawsuits: Potential legal action for damages
- Fines and penalties: Statutory damages for infringement
Business Risks:
- Reputation damage: Negative publicity from legal issues
- Content removal: Loss of work and investment
- Legal costs: Expenses for legal defense
- Business disruption: Interruption of operations
Tools and Resources for Legal Compliance
Use these resources to stay compliant:
Legal Research Tools:
- Copyright databases: Check copyright registration status
- Creative Commons search: Find licensed content
- Public domain resources: Identify free-to-use images
- Legal databases: Research relevant case law
Compliance Software:
- Copyright checkers: Tools to verify image rights
- License trackers: Manage usage rights and restrictions
- Attribution generators: Create proper credit lines
- Compliance monitoring: Track usage and permissions
When to Seek Legal Advice
Consider consulting a lawyer when:
- Commercial use: Using images for business purposes
- Large-scale scraping: Downloading many images
- Unclear rights: Uncertain about image ownership
- International use: Using images across different jurisdictions
- Legal threats: Receiving cease and desist notices
Conclusion: Responsible Image Scraping
Image scraping can be legal when done responsibly:
🎯 Key Takeaways:
- Always check copyright status before downloading images
- Respect website terms and robots.txt files
- Use fair use exceptions appropriately and responsibly
- Get proper licenses for commercial use
- When in doubt, ask permission from image owners
- Document your compliance efforts and legal basis
💡 Use ConvertifyHub Responsibly
ConvertifyHub's image extractor is designed to help you download images legally and responsibly. Our tool respects website resources and provides features to help you identify and respect image rights. Always use our tool in compliance with applicable laws and website terms.
Related Articles

The Complete Guide to Modern Image Formats: WebP, AVIF, and Beyond
Discover the latest image formats that can reduce file sizes by up to 50% while maintaining superior quality. Learn when and how to use WebP, AVIF, and JPEG XL.
Image Batch Processing: Automating Your Workflow
Streamline your image processing workflow with advanced batch operations. Learn to resize, convert, and optimize hundreds of images simultaneously while maintaining quality.
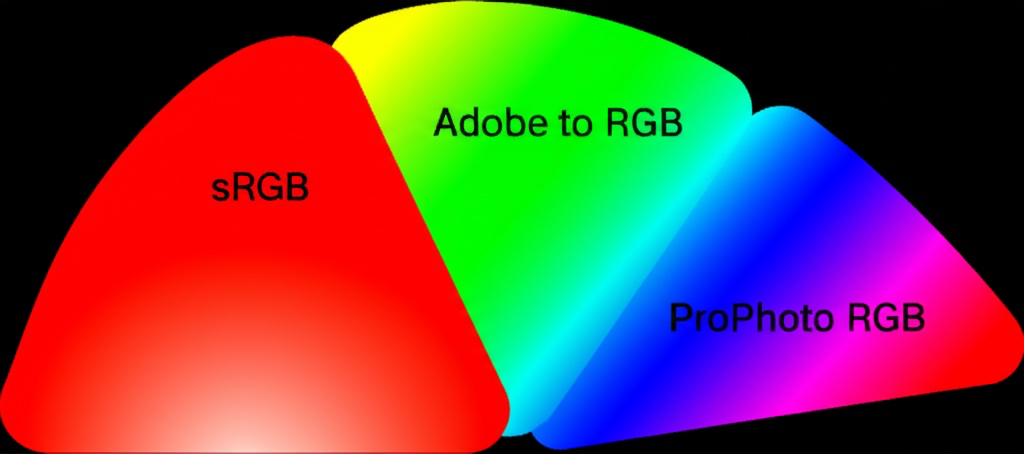
Color Space Conversion: Managing Digital Color Accuracy
Master color space conversion between sRGB, Adobe RGB, ProPhoto RGB, and CMYK. Ensure accurate colors across different devices, media, and printing processes.
Stay in the Loop
Get weekly insights on file conversion, optimization tips, and industry trends.
The Complete Guide to Modern Image Formats: WebP, AVIF, and Beyond
Audio File Conversion: From Lossless to Streaming Formats
QR Code Generation: Best Practices and Advanced Techniques
PDF Optimization: Reducing File Size Without Quality Loss
Video Format Conversion: From Legacy to Modern Codecs
Community Stats
Article Details
Related Tags
Ready to Master File Conversion?
Join thousands of professionals who trust ConvertifyHub for their file conversion needs. Start exploring our comprehensive guides today.